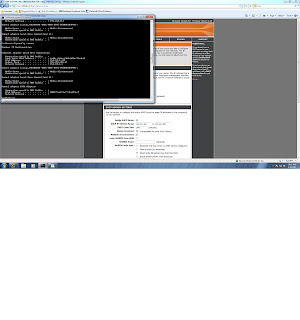
1. Issue a Ipconfig command at the command prompt. Try some of the popular switches such as /all and /?. Capture a screen shot and write a paragraph about how you would use the command to troubleshoot a problem. Put this information in your blog.
You can use Ipconfig to check your IP addressing. Ipconfig /? Will show you all the commands and a brief description of what they do. Use Ipconfig /all to list information such as IPv4 and IPv6 address, subnet mask, default gateway, subnet mask, MAC address, etc. If you are using DHCP, you can use ipconfig /renew to obtain a new IP address.
Sample of ipconfig /all
2. Issue a Netstat command at the command prompt. Try some of the popular switches such as - p and -a. Capture a screen shot and write a paragraph about how you would use the command to troubleshoot a problem. Put this information in your blog.
Using Netstat is great for troubleshooting if you are having problems with latency (lag). It can give you information about current TCP/IP connections such as what port a connection is on and if it is active or just listening. You can also get statistics about protocol types such as sent and received.
3. Issue a Nbtstat command at the command prompt. Try some of the popular switches such as - r and -a. Capture a screen shot and write a paragraph about how you would use the command to troubleshoot a problem. Put this information in your blog.
Nbstat is pretty limited due to the fact that it can only be used on a machine with a Windows based OS and that NetBIOS needs to be running over TCP/IP to get the full benifit. It can do some nice diagnostic work. Nbstat -a Joe will give you the IP address of the machine named Joe on your network. Nbstat -A 192.168.15.1 will give you the name of the machine on your network that has that IP address. If you dont have a Windows system, this command will do you no good.
4. Issue a Hostname command.
Using the hostname command by itself will return the host name of the current client. If you wanted to rename a client to JPBigBoat, you would type hostname JPBigBoat.
5. Use the Nslookup command to view the IP address of at least three domain names. Capture a screen shot and list the class of IP address for each domain. Put this information in your blog.
google.com is a Class A IP
hotmail.com is a Class A IP
ibm.com is a Class B IP
6. Issue a Tracert command at home. Capture a screen shot and write a paragraph about how you would use the command to troubleshoot a problem. Put this information in your blog.